| Catalogue number |
C108733 |
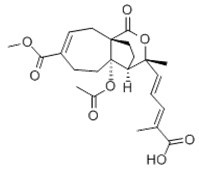
| Chemical name | Pseudolaric Acid B |
| CAS Number | 82508-31-4 |
| Synonyms | |
| Molecular Weight | C23H28O8 |
| Formula | 432.4 |
| Purity | 98% |
| Physical Description | White cryst. |
| Solvent | Chloroform, Dichloromethane,DMSO |
| Storage | Stored at 2-8°C, Protected from air and light, refrigerate or freeze |
| Applications | Pseudolaric acid B (PAB), a diterpene acid isolated from the bark of Pseudolarix kaempferi Gordon, which displays interesting antifungal, antifertility, and cytotoxic activity against multidrug resistant cell lines.
PAB has diverse effects that are relevant to cancer therapy, including inducing apoptosis of cancer cells (IC50 = ~1 μM), preventing angiogenesis, and inhibiting tumor growth in vivo. PAB induces cell cycle arrest at G2-M transition, leading to apoptosis. The drug disrupts cellular microtubule networks and inhibits the formation of mitotic spindles. Polymerization of purified bovine brain tubulin was dose-dependently inhibited by PAB. Furthermore, PAB circumvents the multidrug resistance mechanism, displaying notable potency also in P-glycoprotein–overexpressing cells. PAB can dramatically suppress the AGS cell growth by inducing apoptosis after G2/M phase arrest. These findings are consistent with the possibility that G2/M phase arrest is mediated by the down-regulation of cdc2 levels. The data also suggest that pseudolaric acid B can trigger apoptosis by decreasing Bcl-2 levels and activating caspase-3 protease. The future development of PAB as a cancer therapeutic.
Shown to activate peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) α, γ, and δ-isoforms equipotently (EC50 ~ 100 µM) in CV-1 and H4IIEC3 mammalian cell lines.
PAB significantly suppressed proliferation of DU145 cells in a dose-dependent manner without obvious cytotoxicity. IC50 values of 0.89 +/- 0.18 and 0.76 +/- 0.151 mu M at 48 h was determined by Cell counting kit (CCK-8) assay and clone formation assay, respectively. PAB also induced DU145 cells apoptosis as confirmed by typical morphological changes and Annexin V-FITC staining. PAB may inhibit growth of HRPC DU145 cells and induce apoptosis through ROS generation and Bcl-2 degradation via the activation of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway.
|
| References | 1. Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry, 1989, 27(11), 1025-1030.
2. J. Nat. Prod., 1995, 58(1), 57-67.
3. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129(47), 14556-14557.
|
| Guestbook |
|
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the product adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
| Size | Price(USD) | Discount |
| 5mg | Inquiry | N/A |
| 10mg | Inquiry | N/A |
| 25mg | Inquiry | N/A |
Orders can be placed by Emails. All orders received will be shipped in the next day if the stock is available.
To place an order, please provide the following information.
1) Your name and telephone number
2) Purchase order number
3) Product number, package size, description, and quantity
4) Shipping and billing addresses
Sent to your order to our email: info@coompo.com
If you have any questions about discounts or dealer discount, please send us a message. We will be glad to help.