| Catalogue number | C108812 |
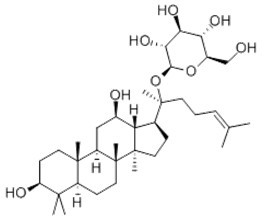
| Chemical name | Ginsenoside Compound K |
| CAS Number | 39262-14-1 |
| Synonyms | 20(S)-Protopanaxadiol 20-O-D-glucopyranoside |
| Molecular Weight | C36H62O8 |
| Formula | 622.8 |
| Purity | 98% |
| Physical Description | White powder |
| Solvent | Chloroform, Dichloromethane,DMSO |
| Storage | Stored at 2-8°C, Protected from air and light, refrigerate or freeze |
| Applications | Ginsenoside compound K (C-K) is an intestinal microbiota metabolite of ginsenoside Rb1, a major constituent in American ginseng. The effects of Rb1 and C-K on the proliferation of HCT-116 and SW-480 human colorectal cancer cells were compared using an MTS assay. Cell cycle and cell apoptosis were assayed using flow cytometry. Enzymatic activities of caspases were determined by colorimetric assay, and interactions of C-K and caspases were explored by docking analysis. C-K showed significant anti-proliferative effects in HCT-116 and SW-480 cells at concentrations of 30-50 µM. At the same concentrations, Rb1 did not show any effects, while C-K arrested the cells in the G1 phase, and significantly induced cell apoptosis. Compared to HCT-116 (p53 wild-type), the p53 mutant cell line SW-480 was more sensitive to C-K as assessed by cell cycle regulation and apoptosis induction. C-K activated expression of caspases 8 and 9, consistent with docking analysis. The docking data suggested that C-K forms hydrogen bonds with Lys253, Thr904 and Gly362 in caspase 8, and with Thr62, Ser63 and Arg207 in caspase 9. C-K, but not its parent ginsenoside Rb1, showed significant anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects in human colorectal cancer cells. These results suggest that C-K could be a potentially effective anti-colorectal cancer agent.
|
| References | 1. Int. J. Oncol., 2012, 40(6), 1970-1976. 2. Cancer Cell International, 2013, 13, 24. 3. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2012, 60(41), 10278-10284. 4. Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 2005, 28(4), 652-656. |
| Guestbook |
| C108532 | Chlorogenic acid | $40.00/20mg |
| C108535 | Isochlorogenic acid B | $110.00/20mg |
| C100277 | Artemisinic acid | $166.00/20mg |
| C104063 | Quercetin-3-O-glucuronide | $286.00/10mg |
| C104290 | 4-O-Feruloylquinic acid | $470.00/5mg |
| Size | Price(USD) | Discount |
| 20mg | $126.00 | 5% OFF |
| 50mg | $290.00 | 8% OFF |
| 100mg | $493.00 | 15% OFF |
To place an order, please provide the following information.
1) Your name and telephone number
2) Purchase order number
3) Product number, package size, description, and quantity
4) Shipping and billing addresses
Sent to your order to our email: info@coompo.com